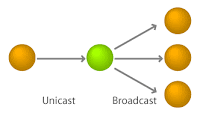
You need to do is answer five simple questions:
- How many subnets does the chosen subnet mask produce?
- How many valid hosts per subnet are available?
- What are the valid subnets?
- what's the broad cast address of each subnet?
- what are the valid hosts in each subnet?